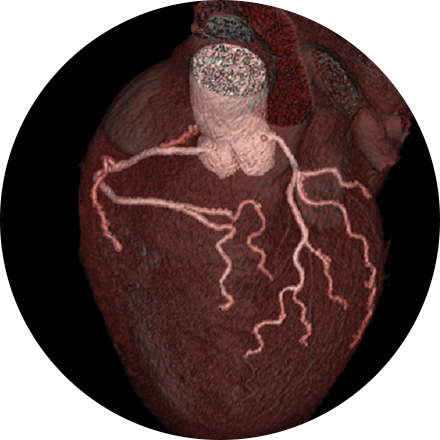
Cardiac imaging has advanced to allow for detection of problems that often could have been done previously only with invasive surgery. Radiologists can detect abnormalities at an earlier stage and then collaborate with physicians in other subspecialties to provide minimally-invasive treatments where applicable.
Some Cardiac & Vascular Imaging Procedures Include:
Carotid ultrasound uses sound waves to produce pictures of the carotid arteries in the neck which carry blood from the heart to the brain. A Doppler ultrasound study, a technique that evaluates blood flow through a blood vessel, is usually a part of this exam. It is most frequently used to screen patients for blockage or narrowing of the carotid arteries which may increase the risk of stroke.
This exam is part of a sophisticated high-speed CT exam of the heart. During the scan, which takes just seconds, the equipment measures the amount of calcium present and calculates a score. The lower the score, the lower the potential risk of an adverse future cardiac injury. (Calcium often covers the atherosclerotic plaque that builds up inside arteries. This plaque and calcium can lead to narrowing of the inside of the arteries which could in turn lead to an increased risk of angina, and a heart attack.) This test can assess coronary heart disease, which is often asymptomatic and is the most common cause of death for patients in the United States.
A multi-gated acquisition (MUGA) scan creates video images that show whether the lower chambers (ventricles) of the heart are pumping blood properly. MUGA uses intravenous material (radiotracers) to show how blood moves through the heart. MUGA can be used to check for pre-existing cardiac conditions prior to chemotherapy, or after treatment to assess possible side effects.
This non-invasive exam shows how well blood perfuses (flows through) your heart muscle—in other words, how well your heart is pumping. Sometimes known as a nuclear stress test, it can be performed while the patient exercises on a treadmill or, if that is inadvisable, using a medicine that simulates the effect of exercise on the heart. Myocardial perfusion is an effective way to assess narrowed arteries, the effects of a past heart attack, or the viability of further procedures, such as a stent.





