New Jersey Imaging Network's Comprehensive Cardiac Imaging Program is New Jersey’s most robust, non-invasive, outpatient, cardiac imaging program.
Our Cardiac Services
Cost Advantage
From our unmatched fleet of advanced, low-dose Cardiac CT units, to our highly trained clinical and support staff, our Comprehensive Cardiac Imaging Program offers New Jersey's cardiology patients only the very best in diagnosis.
New Jersey Imaging Network offers affordable, high-quality, non-invasive cardiac imaging at a cost that is up to —50% lower than that of hospitals.
Safety & Comfort is Our Top Priority
Early detection can lead to more treatment options and a more favorable outcome. Our cardiac imaging program provides a comprehensive evaluation of the heart, including its structure, function, blood flow, and tissue perfusion.
Our low-dose Cardiac CT exams, performed using state-of-the-art imaging technology, help cardiologists develop personalized treatment plans based on each patient's cardiac anatomy and function.
Accurate Diagnosis
Leading-edge cardiac imaging techniques, such as Coronary Computed Tomography Angiography (CCTA), offer several advantages, including a more accurate diagnosis.
Our Comprehensive Cardiac Imaging Program utilizes leading-edge technology to capture high-resolution images of the heart's structures and morphology, allowing our expert cardiac radiologists to analyze robust data and deliver the most precise diagnoses of various heart conditions.
Our Cardiac Radiologists
Cardiac Scheduling
Phone: 800-930-6759
What is CT Cardiac Calcium Scoring?
One of our most accessible and valuable cardiac offerings is our low-cost, Low-Dose CT Cardiac Calcium Scoring exam.
Covered by most insurances, CT Cardiac Calcium Scoring is a simple, non-invasive test that measures the amount of calcified plaque in your heart’s arteries. This specialized CT scan can help determine your risk of heart disease and heart attack.
It is important to note that a CT Cardiac Calcium Scoring exam is not diagnostic in itself. It is a screening exam and is typically used as a first line of detection and in combination with clinical evaluation by a cardiologist and other diagnostic tests, such as Coronary CTA (CCTA), to identify and evaluate the patient's risk of developing heart disease.
Benefits:
- Non-invasive
- Exam only takes a few seconds
- Low radiation
- Screening of the coronary arteries for calcified plaques
Who Should Consider CT Coronary Calcium Scoring:
- Men age 40-65
- Women age 50-70
- Patients at intermediate risk
When to Consider Starting to Screen:
- Age 40 in men and 50 in women
- 10 years before the age of a first-degree relative diagnosed with coronary artery disease (CAD)
Key Insights:
- Low-to intermediate-risk patients who score a "0" can often be managed with diet, exercise, and sometimes medical therapy
- Does not detect non-calcified plaque
- Patients with prior coronary artery bypass grafts and stents or who have known CAD, are not candidates for Calcium Scoring
What is Carotid Ultrasound?
Carotid Ultrasound uses sound waves to produce pictures of the carotid arteries in the neck which carry blood from the heart to the brain. It is most frequently used to screen patients for blockage or narrowing of the carotid arteries which may increase the risk of stroke.
What is Ultrasound Echocardiogram (TTE)?
Ultrasound Transthoracic Echocardiogram is a diagnostic imaging test that uses high-frequency sound waves (Ultrasound) to create comprehensive images of the heart. The exam also includes Doppler Ultrasound, which measures the speed and direction of blood flow, helping to detect abnormal patterns and how well your heart is functioning.
Two of the Most-Common Reasons (Indications) for TTE:
- Suspected Heart Valve Disease: Issues such as mitral valve prolapse, aortic stenosis, or other valve abnormalities
- Unexplained Chest Pain or Shortness of Breath: Evaluates cardiac causes like heart failure or pericardial effusion
TTE Helps Your Health Care Team Find Out:
- The size and shape of your heart, and the size, thickness and movement of your heart’s walls
- How your heart moves during heartbeats
- How well your heart is pumping blood
- If blood is leaking backwards through your heart valves (regurgitation)
- If the heart valves are too narrow (stenosis)
- If a tumor or infectious growth is around your heart valves
Key Insights:
- Low-cost, high-quality, and widely available tool
- Used for both initial diagnosis and ongoing management of cardiovascular disease
- If results are inconclusive or demonstrate abnormalities, a provider may refer for advanced imaging like Coronary CTA (CCTA) or Cardiac MRI
What is CCTA?
CCTA is a heart imaging test that provides highly detailed images of the coronary arteries and anatomical data about the structure of the coronary arteries and the heart.
It helps to determine if plaque buildup has narrowed the coronary arteries (the blood vessels that supply the heart), which may cause chest pain or a heart attack. A referring provider may recommend a CCTA if calcified plaque has already been detected in the coronary arteries.
Benefits:
- Reliable alternative to invasive coronary angiography
- No radiation is left in your body after the scan is finished
- Provides very detailed images of many types of tissue
- Cost-effective for a wide range of medical problems
- Less sensitive to patient movement than MRI
- Implanted medical devices will not prevent the procedure
Who is CCTA for:
- Abnormal anatomy of the coronary arteries
- Low or intermediate-risk for coronary artery disease (CAD)
- Chest pain
- New or worsening symptoms with a previous normal stress test result
American Heart Association and the American College of Cardiology Risk Calculator
How CCTA with FFR CT works:
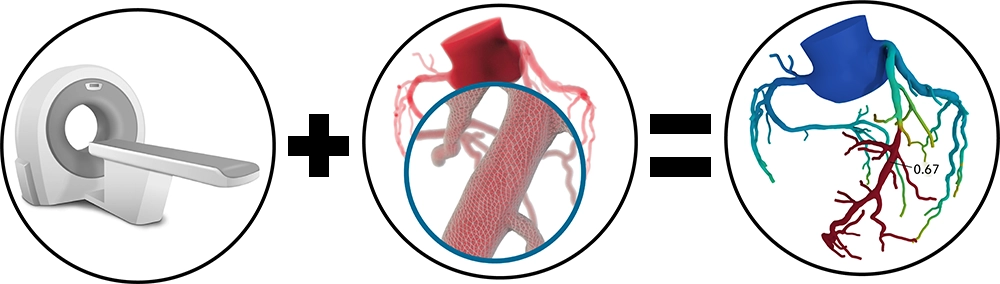
CT with Fractional Flow Reserve (FFR CT) is a physiologic simulation technique that models coronary flow from routine Coronary CT Angiography (CTA). At New Jersey Imaging Network , FFR CT is always interpreted in correlation with clinical and anatomic Coronary CTA findings.
FFR CT increases the specificity in the detection and evaluation of CAD, and decreases the prevalence of non-obstructive disease in invasive coronary angiography (ICA), which helps with decisions regarding revascularization vs. pharmacologic or other forms of treatment.
How can CCTA with FFR CT Help:
- Increases specificity in the evaluation of coronary artery disease
- Reduces unnecessary exposure to radiation or complications from more invasive procedures
- Enables improved clinical decision-making
- Helps guide treatment for patients with CAD
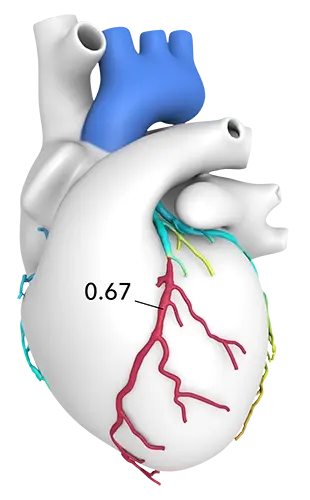
Who is CCTA with FFR CT for:
A physician may request the addition of an FFR CT analysis to a CCTA, because of its ability to add functional information to the anatomical information provided by the CCTA.
Indications for Performing FFR CT:
- Patients with 40-90% stenosis on a Coronary CTA in the setting of uncertain physiologic significance
Key Insights:
- Both anatomical and functional information provided allows for precise evaluation of the severity of CAD
- Can assist physicians with personalized treatment strategies
- Reduces likelihood for additional invasive follow-up studies
- Non-invasive
- According to a study published by the National Institute of Health (NIH), CCTA with added FFR CT “led to a reduction in (invasive) diagnostic testing and less revascularizations”
What is MUGA?
A multi-gated acquisition (MUGA) scan creates video images that show whether the lower chambers (ventricles) of the heart are pumping blood properly. MUGA uses intravenous material (radiotracers) to show how blood moves through the heart. MUGA can be used to check for pre-existing cardiac conditions prior to chemotherapy, or after treatment to assess possible side effects.